Saturday, February 26, 2011
secure sockets layer
Transport Layer Security and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer, are cryptographic protocols that provide security for communications over networks such as the Internet.
Friday, February 25, 2011
copyright
is the relatively recent extension of copyright law to machine readable software. While many of the legal principles and policy debates concerning software copyright have close parallels in other domains of copyright law, there are a number of distinctive issues that arise with software.
feed
is a family of web feed formats used to publish frequently updated works such as blog entries, news headlines, audio, and video in a standardized format.
Directories
In computer software, specifically the command line interface of the OpenVMS operating system, the DIRECTORY command is used to list the files inside a directory.
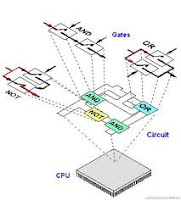
boolean Logic
Boolean Logic is considered to be the basic of digital electronics. A computer’s most basic operation is based on digital electronics. Most operations which only humans could do, is now being done by computers.
Blog
A blog is a type of website, usually maintained by an individual with regular entries of commentary, descriptions of events, or other material such as graphics or video. Entries are commonly displayed in reverse-chronological order.
Wiki
Wiki software is software that runs a wiki, or a website that allows users to collaboratively create and edit web pages using a web browser. A wiki system is usually a web application that runs on one or more web servers.
webapp
In software engineering, a web application is an application that is accessed via a web browser over a network such as the Internet or an intranet.
Website
A website is a collection of related web pages containing images, videos or other digital assets. A website is hosted on at least one web server, accessible via a network such as the Internet or a private local area network through an Internet address also called URL.
Web Cache
Web caching is the caching of web documents to reduce bandwidth usage, server load, and perceived lag. A web cache stores copies of documents passing through it; subsequent requests may be satisfied from the cache if certain conditions are met.
Web 2.0
The term Web 2.0 is commonly associated with web applications that facilitate interactive information sharing, interoperability, user-centered design, and collaboration on the World Wide Web.
uniform resource locator (URL)
In computing, a uniform resource locator (URL) is a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) that specifies where an identified resource is available and the mechanism for retrieving it.
Social Networking Site
A social network service is an online service, platform, or site that focuses on building and reflecting of social networks or social relations among people.
Really Simple Syndication(RSS)
is a family of web feed formats used to publish frequently updated works such as blog entries, news headlines, audio, and video in a standardized format.
Portal
A web portal, also known as a links page, presents information from diverse sources in a unified way.
Podcast
A podcast is a series of digital media files (either audio or video) that are released episodically and often downloaded through web syndication.
Internet Service Provider (ISP)
An Internet service provider (ISP), also sometimes referred to as an Internet access provider, is a company that offers its customers access to the Internet.
Internet Protocol (IP) Address
An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a numerical label that is assigned to devices participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication between its nodes.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an Application Layer protocol for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems.
Hypertext Markup Language (MTML)
Stands for HyperText Markup Language (MTML), is the predominant markup language for web pages. It provides a means to create structured documents by denoting structural semantics for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists etc as well as for links, quotes, and other items.
Home Page
The home page is the URL or local file that automatically loads when a web browser starts or when the browser's "home" button is pressed. One can turn this feature off and on, as well as specify a URL for the page to be loaded.
hit
The Hit is a simple, yet sophisticated application to manage the daily chaos of your modern life. Based on the simple concept of making lists, The Hit List lets you plan, forget, then act when the time is right.
Geographic Imaging
Is any system that captures, stores, analyzes, manages, and presents data that are linked to location. In the simplest terms,is the merging of cartography, statistical analysis, and database technology.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
Protocol that allows users to copy files between their local system and any system they can reach on the network.
Domain
The Domain Name System is a hierarchical naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participants.
Digital Certificate
A data file that is issued by a Certification Authority to an individual or organisation to identify them to online services.
Cookie
A short line of text that a web site puts on your computer's hard drive when you access the web site.
Client
A client is an application or system that accesses a remote service on another computer system, known as a server, by way of a network. The term was first applied to devices that were not capable of running their own stand alone programs, but could interact with remote computers via a network.
ActiveX
ActiveX is a framework for defining reusable software components that perform a particular function or a set of functions in Microsoft Windows in a way that is independent of the programming language used to implement them.
Saturday, February 19, 2011
virus
A computer virus is a computer program that can copy itself and infect a computer. The term virus is also commonly but erroneously used to refer to other types of malware, adware, and spyware programs that do not have the reproductive ability.
Urban Legend
the definitive Internet reference source for urban legends, folklore, myths, rumors, and misinformation. Use the search box above to locate your item of interest, or click one of the icons below to browse the site by category.
Trojan Horse
that appears to perform a desirable function for the user but instead facilitates unauthorized access to the user's computer system.
Time Bomb
In computer software, a time bomb refers to a computer program that has been written so that it will stop functioning after a predetermined date or time is reached.
teleconferencing
A teleconference is the live exchange and mass articulation of information among several persons and machines remote from one another but linked by a telecommunications system.
Tagging
Tag In online computer systems terminology, a tag is a non-hierarchical keyword or term assigned to a piece of information such as an internet bookmark, digital image, or computer file. This kind of metadata helps describe an item and allows it to be found again by browsing or searching.
spam
Spam is the abuse of electronic messaging systems including most broadcast media, digital delivery systems to send unsolicited bulk messages indiscriminately.
RDF Summary
The resource disciption framework (RDF) is a family of World Wide Web Consortium specifications originally designed as a metadata data model. It has come to be used as a general method for conceptual description or modeling of information that is implemented in web resources, using a variety of syntax formats.
Pyramid Schemes
A pyramid scheme is a non-sustainable business model that involves the exchange of money primarily for enrolling other people into the scheme, without any product or service being delivered. Pyramid schemes are a form of fraud.
phishing
In the field of computer security, phishing is the criminally fraudulent process of attempting to acquire sensitive information such as usernames, passwords and credit card details by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication.
Netiquette
Netiquette is a set of social conventions that facilitate interaction over networks, ranging from Usenet and mailing lists to blogs and forums.
Logic Bomb
is a computer program that lies dormant for a period of time in a systems and is triggered by an event, such as a date.
hoax
Explicitly meaning, in a technical sense of network security research, a form of chain letter, carrying a false warning of a internet security threat that doesn't exist.
Fraud
Internet fraud refers to the use of Internet services to present fraudulent solicitations to prospective victims, to conduct fraudulent transactions, or to transmit the proceeds of fraud to financial institutions or to others connected with the scheme. Internet fraud can occur in chat rooms, email, message boards or on websites.
Filtering
A filter is a computer program to process a data stream. Some operating systems such as Unix are rich with filter programs.
Windows Mail
Windows Mail is an e-mail and newsgroup client included in Windows Vista, that was superseded by Windows Live Mail. It is the successor to Outlook Express.
User Agent
A user agent is a client application implementing a network protocol used in communications within a client-server distributed computing system.
text messaging
Text messaging, also known as texting, refers to the exchange of brief written messages between mobile phones over cellular networks.
Spam
Spam is the abuse of electronic messaging systems including most broadcast media, digital delivery systems to send unsolicited bulk messages indiscriminately.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)